By Sangamesh B Satihal, Oracle DBA
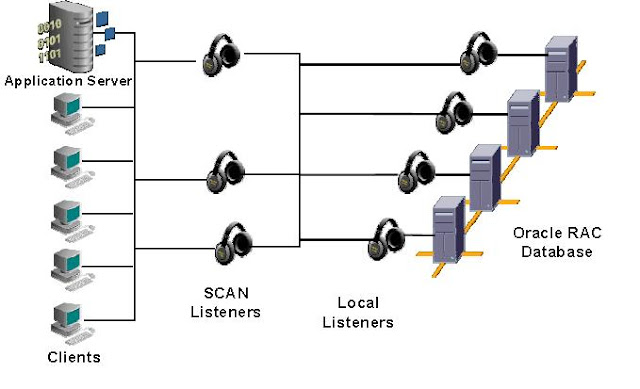
SCAN is a new feature of 11gR2 that
provides a user or client to connect to the cluster(RAC database) using sinlge
virtual hostname. This virtual hostname is called as SCAN and this will work as
cluster alias for a database in the cluster. This SCAN needs to be resolved to
minimun one IP address but oracle strongly recommends three IP addresses.
In previous releases(10g and 11gR1), whenever
user has to connect RAC database, he was supposed to connect using virtual IPs
through VIP listener and each instance in a cluster had it's own virtual IP to
connect to the database. But note that even we could connect RAC database using
public IP also but our purpose of high availability will be lost if we use
public IP. So if there are n number of
instances, we had n number of VIPs and same should be used by a client in his
TNS entry. It impies that when we add or remove a node or nodes from a cluster,
then client has to update his tns enty in his tnsnames.ora file. In order to
avoid this, Oracle introduced SCAN concept. By using which client can use only
one host to connect to cluster database, independenet of how many instances are
running on that cluster. One more advantage of SCAN is it automatically provides both failover and load
balancing of connects, where the new connection will be directed to the least
busy instance in the cluster by default. Having a single name to access the
cluster allows clients to use the EZConnect client and the simple JDBC thin URL
to access any database running in the cluster, independently of which server(s)
in the cluster the database is active.
RAC Instances register to SCAN listeners as remote listeners. Example of
EZconnect method in oracle and JDBC connection is shown below.
EZconnet :sqlplus
system/manager@testdb-scan:1521/testdb
( EZconnecxt
format is CONNECT username/password@[//]host[:port][/service_name])
JDBC connect: jdbc:oracle:thin:@testdb-scan:1521/testdb
Note : Since EZconnect is used with SCAN,
the SQLNET.ora file should include EZconnect as one of the naming methods, for
example:
NAMES.DIRECTORY_PATH=(tnsnames,ezconnect,ldap)
How
SCAN works
For clients connecting using Oracle
SQL*Net 11g Release 2, three IP addresses will be received by the client by resolving
the SCAN name through DNS. The client will then go through the list it receives
from the DNS and try connecting through one of the IPs received. If the client
receives an error, it will try the other addresses before
returning an error to the user or
application. This is similar to how client connection failover works in
previous releases when an address list is provided in the client connection
string. When a SCAN Listener listening on a SCAN IP address receives a
connection request, Because all services on the cluster are registered with the
SCAN listener, the SCAN listener checks with VIP listener(local listener) and
replies with the address of the local listener on the least-loaded node (Each
scan listener keeps updated cluster load statistics) where the service is
currently being offered to the client. Finally, the client establishes
connection to the service through the listener on the node where service is
offered. All of these actions take place transparently to the client without
any explicit configuration required in the client.
How
we can configure SCAN
The SCAN is configured during the
installation of Oracle Grid Infrastructure that is distributed with Oracle
Database 11g Release2. Oracle Grid Infrastructure is a single Oracle Home that
contains Oracle Clusterware and Oracle Automatic Storage Management. You must
install Oracle Grid Infrastructure first in order to use Oracle RAC 11g Release
2. During the installation phase of the Oracle Grid Infrastructure
installation, you will be prompted to provide a SCAN name. The default value
for SCAN is cluster_name.GNS_sub_domain, or, cluster_name-scan.domain_name if
GNS is not used. For example, in a cluster that does not use GNS, if your
cluster name is salesRAC, and your domain is example.com, then the default SCAN
address is salesRAC-scan.example.com:1521.
During the installation of Oracle Grid
Infrastructure, several Oracle Clusterware resources are created for SCAN:
A SCAN VIP is created for each IP
address that SCAN resolves to
A SCAN listener is created for each
SCAN VIP
A dependency on the SCAN VIP is
configured for the SCAN listener
SCAN VIPs function like node VIPs,
except that SCAN VIPs can run on any node in the cluster. Also, if you have
three SCAN VIPs but only two nodes in your cluster, you can have two SCAN VIPs
running on the same server. Clients (users or applications) that connect using
SCAN instead of the node VIPs do not have to update the list of VIP addresses
in their local tnsnames.ora file when nodes are added to or removed from the
cluster.
During Oracle Grid
Infrastructure installation, SCAN listeners are created for as many IP
addresses as there are addresses assigned to resolve to the SCAN. Oracle
recommends that the SCAN resolves to three addresses, to provide high
availability and scalability. If the SCAN resolves to three addresses, then
there are three SCAN listeners created.
The addresses for the SCAN
listeners resolve with either the domain name service (DNS), or within the
cluster for the Grid Naming Service (GNS), using a round-robin method. SCAN
listeners can run on any node in the cluster.
The database parameter
LOCAL_LISTENER specifies the listening endpoint of the local database listener,
and the database parameter REMOTE_LISTENER parameter identifies the SCAN
listeners. The database registers with the local and SCAN listeners by using
the connect description information contained in these parameters. Oracle
Database 11g release 2 and later instances only register with SCAN listeners as
remote listeners. Upgraded databases register with SCAN listeners as remote
listeners, and also continue to register with all node listeners.
Starting with Oracle
Database 11g release 2, the REMOTE_LISTENER parameter is always set to the SCAN
address. Do not set it to an Oracle Net alias that has a single address that
uses SCAN for the host name (HOST=scan). For example, if SCAN for the cluster
is myscan, and the GNS subdomain for the cluster is mycluster.example.com, then
the REMOTE_LISTENER parameter has the following value:
myscan.mycluster.example.com:1521
IP Addresses required for RAC 11gr2 configuration are
A Public IP on each node
A Local VIP for each noe
A Privated IP for each
node for Interconnect
SCAN IP for the cluster.
At least one, recommended three.
A Public IP for GNS VIP
You can configure SCAN
Name resolution using :
1. Define the SCAN in your corporate DNS (Domain Name Service)
2. Use the Grid Naming Service (GNS)
1. Define the SCAN in your corporate DNS (Domain Name Service)
Ih this method, hostname which is used
for SCAN will be resolved to 3 IP
addresses using a round-robin algorithm in DNS server. This will be taken care
by system admin or network admin. Three IP addresses are recommended
considering load balancing and high availability requirements regardless of the
number of servers in the cluster. The IP addresses must be on the same
subnet as your public network in the
cluster. The name must be 15 characters or less in length, not including the
domain, and must be resolvable without
the domain suffix (for example: “sales1-scan’ must be resolvable as opposed
to “scan1-scan.example.com”). The IPs
must not be assigned to a network interface (on the cluster), since Oracle
Clusterware will take care of it.
You can check the SCAN configuration
in DNS using “nslookup”. If your DNS is set up to provide round-robin access to
the IPs resolved by the SCAN entry, then run the “nslookup” command at least
twice to see the round-robin algorithm work. The result should be that each
time, the “nslookup” would return a
set of 3 IPs in a different order.
testdb1-scan.example.com IN A 133.21.69.194
IN A 133.21.69.193
IN A 133.21.69.192
2. Use the Grid Naming Service (GNS): GNS is
a Grid naming service that services subdomain. This subdomain is a portion of
the corporate DNS domain.
The only requirement is that a GNS Sub domain must be made and the DNS must be
configured so that each request for this Sub Domain will be delegated to the
GNS Sub domain, so that GNS can handle the request. DNA administrator (Network
admin) creates a subdomain and delegates the subdomain name resolution to GNS.
This DNS subdomain must be created
before grid installation. GNS listens on any fixed IP address of the RAC node
within the cluster for the resolution of the name for that subdomain. The GNS
VIP address is the ip address of the server that will host the GNS. You need to
make sure this one is available for use. This GNS is managed by a CRS agent. GNS and GNS VIP run on any one node of the
cluster and it listens on default port 53. If the node on which GNS was running
fails, then Oracle clusterware fails GNS and along with the GNS VIP to another
node in the cluster.
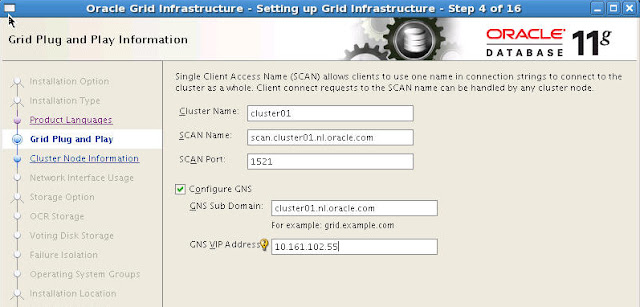
During GRID installation, the option
"Configure GNS" is checked, as shown below, if we are using GNS. If
the option "Configure GNS" is not checked, then DNS will be used for
SCAN name resolution.
After installation you will find three listener processes running
(separated on all cluster nodes). For each SCAN listener there will be a
dedicated network interface running with the same IP as configured in DNS:
Client Connection to database “TESTDB” using SCAN would use this
tnsnames entry:
TESTDB =
(DESCRIPTION=
(ADDRESS=(PROTOCOL=tcp)(HOST=testdbrac-scan.sangam.de)(PORT=1521))
(CONNECT_DATA=(SERVICE_NAME=TESTDB))
)
The ”old fashioned” way, we can connect to db as below
TESTDB_old =
(DESCRIPTION=
(ADDRESS_LIST=
(ADDRESS=(PROTOCOL=tcp)(HOST=testdbrac1-vip.sangam.de)(PORT=1521))
(ADDRESS=(PROTOCOL=tcp)(HOST=testdbrac2-vip.sangam.de)(PORT=1521))
)
(CONNECT_DATA=(SERVICE_NAME=TESTDB))
)
Connecting to a named instance:
TESTDB1 =
(DESCRIPTION=
(ADDRESS=(PROTOCOL=tcp)(HOST=rac-scan.sangam.de)(PORT=1521))
(CONNECT_DATA=(SERVICE_NAME=TESTDB)
(INSTANCE_NAME=TESTDB1))
)

Excellent article. Thanks
ReplyDelete